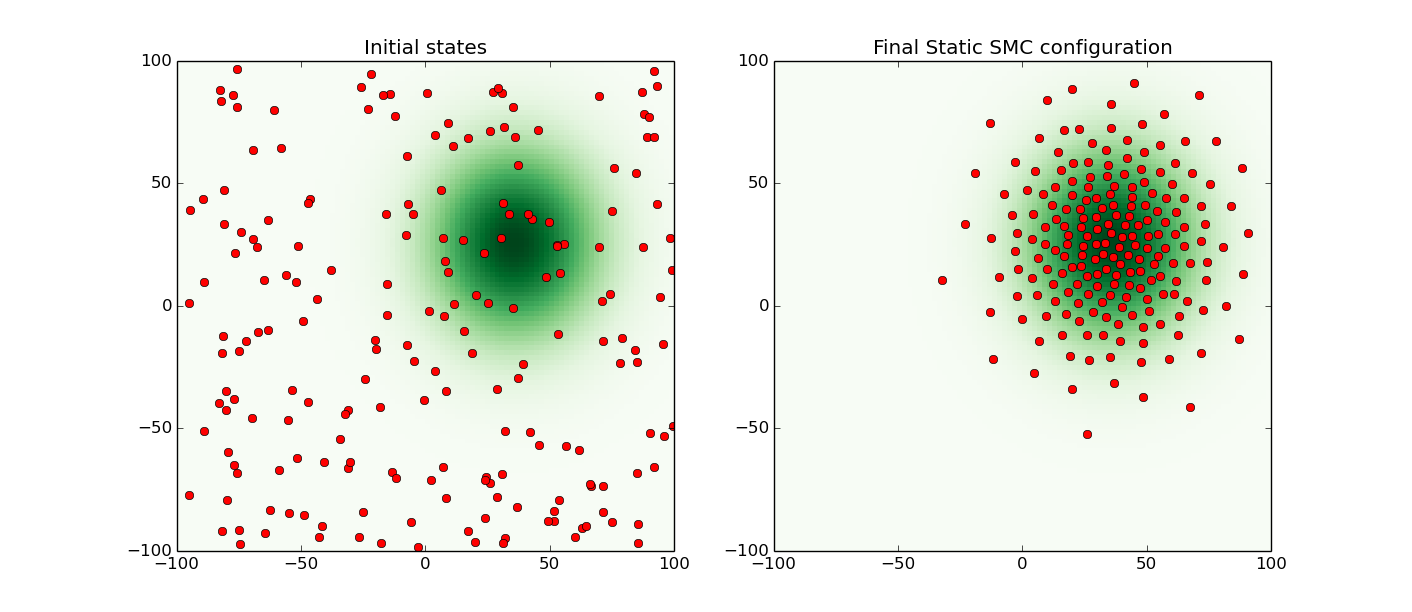
Coverage of a Gaussian distribution
It is possible to use Static SMC to cover non-uniform distributions like the Gaussian distribution. One such example is shown below.
# After necessary imports
# Define probability distribution
xmin, xmax = (-100.0, 100.0)
ymin, ymax = (-100.0, 100.0)
prob_dist = ProbDist(xmin=xmin, xmax=xmax, ymin=ymin, ymax=ymax, Nx=100, Ny=100)
# first set everything to zero
prob_dist.set_zero()
# mean of gaussian distribution
mu_x, mu_y = (35, 25)
mu = np.array([[mu_x], [mu_y]])
# covariance of gaussian distribution
sig_x, sig_y = (35, 40)
cov = np.array([[sig_x*sig_x, 0], [0, sig_y*sig_y]])
# adding gaussian distribution
prob_dist.add_gaussian(mu, cov, 1.0)
# Define StaticSMC coverage object
static_smc = StaticSMC(prob_dist)
# Add agents (with random initial locations) to coverage object
for _ in range(200):
static_smc.add_agent(Agent(random.random(), random.random()))
# Run the algorithm (200 time-steps of size 1)
static_smc.time_steps(200, 1)
Below is shown the initial random locations of the agents and the final optimal configuration obtained using Static SMC. The green coloring represents the Gaussian distribution to be covered. To see the full code for this example, look here.